Aboriginal rights in Canada
Aboriginal legal rights reference practices, practices and traditions that distinguish the unique culture of every First country and were practiced before European contact. These are legal rights that some Aboriginal peoples of Canada hold as a result of their particular forefathers' longstanding usage and occupancy of the land. The rights of particular peoples to hunt, pitfall and seafood on ancestral places are types of Aboriginal legal rights. Aboriginal liberties range from team to team with regards to the customs, techniques and customs having created section of their particular distinctive countries. Aboriginal legal rights tend to be protected under s.35 for the Constitution Act, 1982.
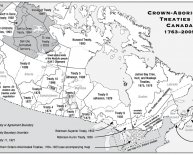
There are areas in Canada where Aboriginal individuals claims to Aboriginal liberties and title have not been dealt with by treaty or in just about any appropriate method. Typically, in many of British Columbia, Yukon and Nunavut, also parts of Québec and Newfoundland and Labrador, treaties weren't created using very first Nations or Inuit people who existed there. To address this fact also outstanding claims of Aboriginal rights and name, the extensive land claims process (and/or making of modern treaties) was established in 1973.